Learning from Noisy Data
[Summary & Contributions] | [Relevant Publications]
Summary and Contributions
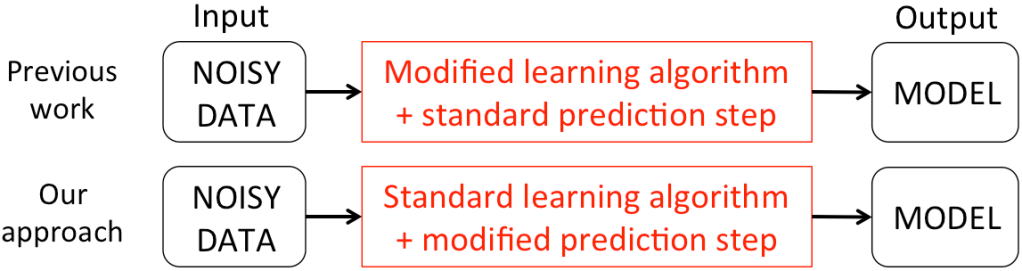
In many applications of machine learning, one receives a noise-corrupted version of the original data as input (e.g. due to errors in data measurement devices or noise in the human data collection/labeling process). In general, the learning process then needs to account for this noise and learn a correct model despite the noisy observations. A particular form of noise that has received interest in recent years is that of class-conditional label noise, where labels are corrupted stochastically according to some noise matrix (this generalizes the random classification noise model studied in previous work). Most previous approaches for this setting require changing the surrogate loss to be optimized by the learning algorithm, which entails a potentially significant change in the code used to implement the algorithm. In contrast, we have developed a noise-corrected plug-in approach that trains a standard class probability estimation algorithm directly on the noisy data, and then applies noise-correction only in the final plug-in step at prediction time; this results in a significantly easier-to-implement algorithm in practice (see figure below). We have also developed noise-corrected algorithms for learning with complex (multivariate/non-decomposable) performance measures in the presence of noisy labels.
Relevant Publications
- Mingyuan Zhang and Shivani Agarwal.
Multiclass learning from noisy labels for non-decomposable performance measures.
In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS), 2024.
[pdf] - Mingyuan Zhang, Jane Lee, and Shivani Agarwal.
Learning from noisy labels with no change to the training process.
In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2021.
[pdf]